Divide and Conquer
이분법 Bisection method 본문
728x90
주어진 구간의 크기를 근이 존재하는 영역을 따라가며 연속적으로 반으로 줄여감구간이 올바르면 확실히 근을 찾음(근의 개수는 몰라, 존재하는지도 몰라)수렴 속도 느림(fa와 fb의 부호를 비교)
import numpy as np
from scipy import optimize
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef f(x):
return np.sqrt(3*x*np.exp(-x)) -0.5
a = 0
b = 3
[x0, fx0] = optimize.bisect(f, a, b, full_output = True)
print('x0 = ', x0, 'f(x0) = ', f(x0))
# x0 = 0.09129978313876563 f(x0) = 1.3097301021502972e-12converged: True 수렴했다는 뜻
반복 횟수로 20을 주면 22가 나온다: a랑 b를 넣어서 계산한 것도 포함되기 때문
root1 = optimize.bisect(f, a,b full_output = True)
print(root1)def f(x):
return 3.0*x - np.cos(x) - 1.0
a = -2.0 # 0
b = 3.0 #5
n = 20 # 30
c = np.zeros(n)
for i in range(n):
c[i] = (a + b)/2.0
fc = f(c[i])
if np.sign(fc) == np.sign(f(a)):
a = c[i]
else:
b = c[i]
print("%5s %8s"%('k', 'c'))
for k in range(n):
print("%5d %9.4f"%(k + 1, c[k]))
k c
1 0.5000
2 1.7500
3 1.1250
4 0.8125
5 0.6562
6 0.5781
7 0.6172
8 0.5977
9 0.6074
10 0.6025
11 0.6050
12 0.6062
13 0.6068
14 0.6071
15 0.6070
16 0.6070
17 0.6071
18 0.6071
19 0.6071
20 0.6071iter = np.arange(0, n)
plt.plot(iter, c)
plt.xlabel('iterations')
plt.ylabel('c')
plt.grid()
plt.show()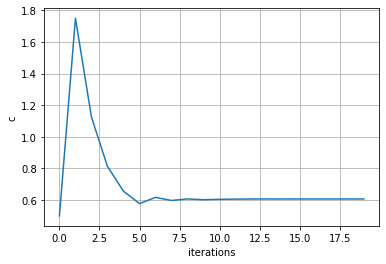
plt.plot(iter,f(c))
plt.xlabel('iterations')
plt.ylabel('f(x)')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
print(f(c[n-1]))
print(f(c[-1]))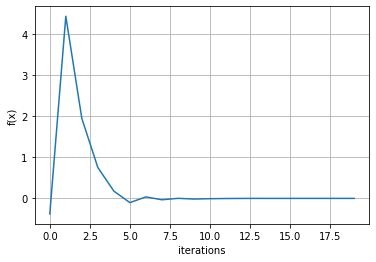
def f(x):
return -(x**2) - 6.0 * x - 5.0
def bisection(a, b, func, max_iter, tol):
a1 = a
b1 = b
c = np.zeros(1)
for i in range(max_iter):
c[i] = (a1 + b1) / 2.0
fc = func(c[i])
if np.sign(fc) == np.sign(func(a1)):
a1 = c[i]
else:
b1 = c[i]
if np.abs(fc) < tol:
return (c, i+1)
c = np.append(c, np.zeros(1))
return (c, i+1)
a = -3.0
b = 3.0
n=20
(c, itr) = bisection(a,b, f, n, 1e-4)
print('iteration = {}'.format(itr))
print(c)
print("x0 = ", c[itr-1], "f(x0) = ", f(c[-1]), "iterations = ", itr)iteration = 17
[ 0. -1.5 -0.75 -1.125 -0.9375 -1.03125
-0.984375 -1.0078125 -0.99609375 -1.00195312 -0.99902344 -1.00048828
-0.99975586 -1.00012207 -0.99993896 -1.00003052 -0.99998474]
x0 = -0.9999847412109375 f(x0) = -6.103538908064365e-05 iterations = 17iter = np.arange(0, itr)
plt.plot(iter, c)
plt.xlabel('iterations')
plt.ylabel('c')
plt.show()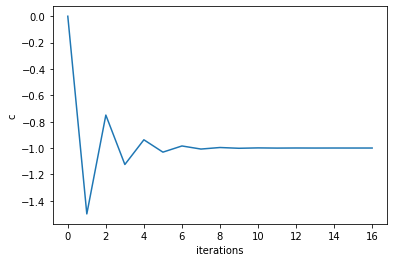
이분법으로 근을 구하시오
$f(x) = \sqrt{3x\ln{x}} + 0.7$
[10, 15]구간 허용 오차 $1 \times 10^{-4}$def f(x):
return np.sqrt( 3*x*np.log1p(x) ) +0.7
a = 10.0
b = 15.0
n = 50
def bisection(a, b, func, max_iter, tol):
a1 = a
b1 = b
c = np.zeros(1)
for i in range(max_iter):
c[i] = (a1 + b1) / 2.0
fc = func(c[i])
if np.sign(fc) == np.sign(func(a1)):
a1 = c[i]
else:
b1 = c[i]
if np.abs(fc) < tol:
return (c, i+1)
c = np.append(c, np.zeros(1))
return (c, i+1)
(c, itr) = bisection(a,b, f, n, 1e-4)
print('iteration = {}'.format(itr))
print(c)
print("x0 = ", c[itr-1], "f(x0) = ", f(c[-1]), "iterations = ", itr)iteration = 50
[12.5 13.75 14.375 14.6875 14.84375 14.921875
14.9609375 14.98046875 14.99023438 14.99511719 14.99755859 14.9987793
14.99938965 14.99969482 14.99984741 14.99992371 14.99996185 14.99998093
14.99999046 14.99999523 14.99999762 14.99999881 14.9999994 14.9999997
14.99999985 14.99999993 14.99999996 14.99999998 14.99999999 15.
15. 15. 15. 15. 15. 15.
15. 15. 15. 15. 15. 15.
15. 15. 15. 15. 15. 15.
15. 15. 0. ]
x0 = 14.999999999999996 f(x0) = 0.7 iterations = 50x = np.linspace(0, 20, 100)
y = f(x)
fa = f(a)
fb = f(b)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.stem([a, b], [fa, fb], use_line_collection = True)
plt.grid()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('f(x)')
plt.show()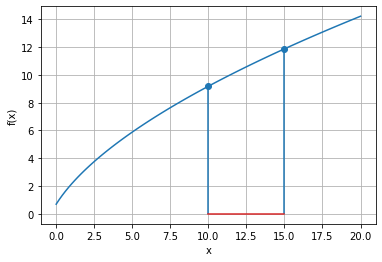
[x0, fx0] = optimize.bisect(f, a, b, full_output = True)
print('x0 = ', x0, 'f(x0) = ', f(x0))---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
~\AppData\Local\Temp/ipykernel_10324/2082474369.py in <module>
----> 1 [x0, fx0] = optimize.bisect(f, a, b, full_output = True)
2 print('x0 = ', x0, 'f(x0) = ', f(x0))
C:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\scipy\optimize\zeros.py in bisect(f, a, b, args, xtol, rtol, maxiter, full_output, disp)
547 if rtol < _rtol:
548 raise ValueError("rtol too small (%g < %g)" % (rtol, _rtol))
--> 549 r = _zeros._bisect(f, a, b, xtol, rtol, maxiter, args, full_output, disp)
550 return results_c(full_output, r)
551
ValueError: f(a) and f(b) must have different signs근을 찾기 위해서는 근이 존재할 가능성이 있는 영역을 찾고 실제로 근을 찾아내는 과정을 거친다 f(10)과 f(15)의 부호가 같기 때문에 근의 존재 여부를 알 수 없다 ` f(a) and f(b) must have different signs`
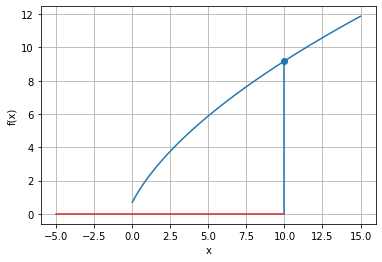
방정식의 근을 구하는 것은 f(c)=0을 만족하는 c를 구하는 것과 같다 하지만 주어진 식은 y축으로 0.7 평행 이동했기 때문에 0이 되는 구간이 없다
반응형
'성장캐 > 수치해석' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 뉴튼랩슨 Newton-Raphson (0) | 2022.04.25 |
|---|---|
| 고정점 방법 Fixed point Method (0) | 2022.04.25 |
| 방정식의 근 구하기 개요 (0) | 2022.04.15 |
| 수학 목차 (0) | 2022.02.28 |
| 오일러공식 (0) | 2021.07.30 |
Comments



